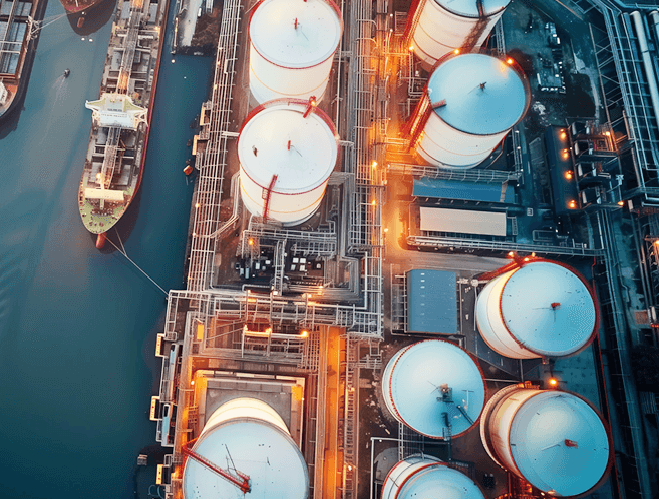
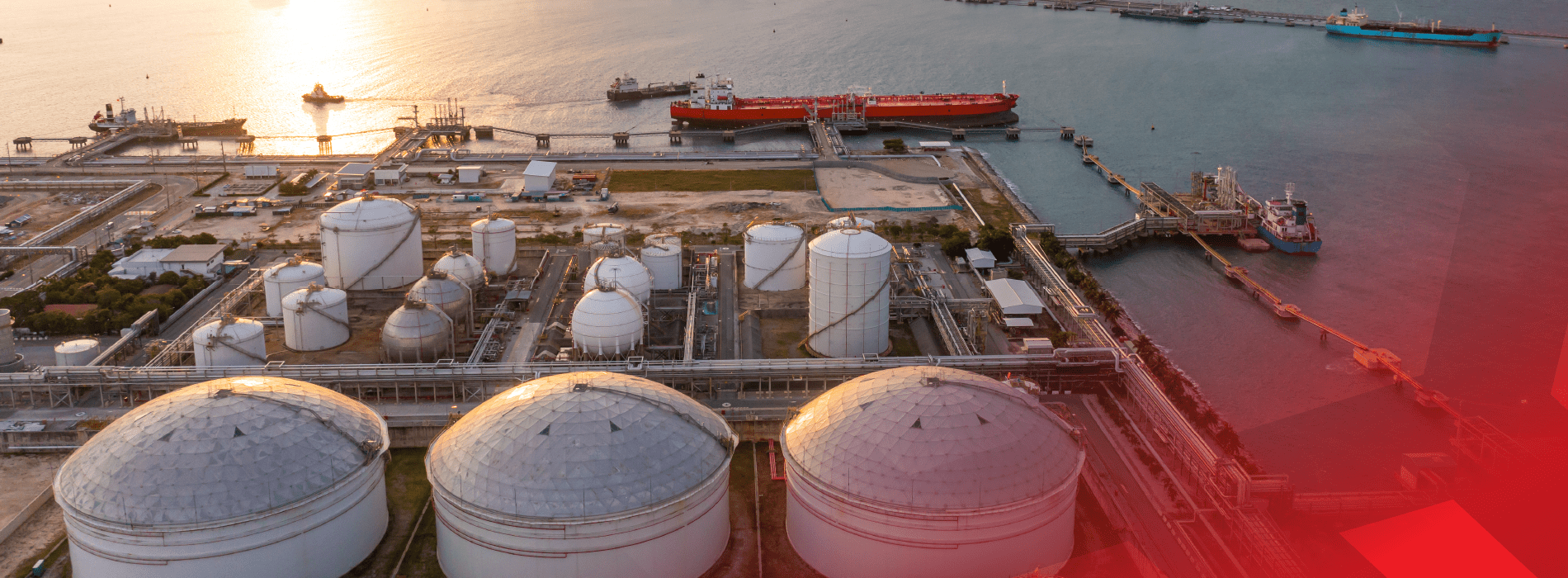
MCG PRODUCTS
Heavy Distillates
Distillate fuel is a type of fuel used for internal-combustion vehicles with either mechanical transmissions or electric transmissions. They are used in automobiles, locomotives and agricultural machinery as well as space heaters and power generators.
- Heavy Fuel Oil Heavy Fuel Oil (HFO) is a category of fuel oils of a tar-like consistency identified as a “worse case substance”. Also known as bunker fuel or residual fuel oil, HFO is the result or remnant from the distillation and cracking process of crude oil. For this reason, HFO is contaminated with several different compounds including aromatics, sulfur and nitrogen, making emission upon combustion more polluting compared to other fuel oils
- Residuum Residue from crude oil after distilling off all but the heaviest components, with a boiling range greater than 1000 degrees Fahrenheit. Road Oil. Any heavy petroleum oil, including residual asphaltic oil used as a dust palliative and surface treatment on roads and highways. It is generally produced in six grades from 0, the most liquid, to 5, the most viscous.
- Wax Residue Wax, which is more popularly known as Foots Oil is a by-product of petroleum. Residue Wax is derived from the production of Semi Refined Paraffin Wax. Its application lies in the rubber industry, plastic industry, polish industry, matchbox industry and more.
- Asphalt/Bitumen Asphalt is produced in a plant that heats, dries and mixes aggregate, bitumen and sand into a composite mix. It is then applied through a paving machine on site as a solid material at a nominated or required thickness, relative to the end use. Asphalt results in a smoother and more durable asphalt road surface than a bitumen-sealed road. Bitumen is a binding agent produced from petroleum. Bitumen is known for being strongly adhesive and resistant to damage from water and oil spills. This makes bitumen the ideal binder for asphalt because asphalt is commonly used as a surface for roads, car parks and driveways. Bitumen can be produced to different specifications depending on how it’s going to be used but in all cases, bitumen is created by distilling crude oil. This process removes the lighter liquid and leaves a thick sticky substance that, in the case of asphalt, will hold heavy aggregate like stones and gravel with sand. Bitumen can also be confused with tar, which is another binding agent that when mixed with aggregate, makes tarmac. Bitumen is actually the liquid binder that holds asphalt together. The term bitumen is often mistakenly used to describe asphalt. A bitumen-sealed road has a layer of bitumen sprayed and then covered with an aggregate. This is then repeated to give a two-coat seal.
- Lubricating Oils Lubricating oil is a class of refined products used to reduce friction and wear between bearing metallic surfaces. It is distinguished from other fractions of crude oil by its high (>340°C) boiling-point region. There are two basic categories of lubricating oil: mineral and synthetic. Mineral oils are lubricating oils refined from naturally occurring crude oil. Synthetic oils are lubricating oils that are manufactured.
1
Flexible Operational Solutions
Leveraging our expertise, we ensure compliance with local and international regulations, enhancing transparency and ensuring business sustainability and balance across various operational environments.
Read MoreOUR PARTNERS